eXtending the Reality of Museum with XR
- 10 minutes read - 1960 wordseXtended Reality (XR/AR/VR) technology is changing the reality of almost every industry today by enhancing user experiences. XR adoption in the museum industry is also quite natural, let’s understand how it is shaping up the Museums of Future.

Museum is a place that displays artifacts from history, culture, science, art and more. As per International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are around 55000 museums worldwide designed with different themes serving different types of artifacts. The museums are all about providing user experience where visitors immerse in the environment provided. Over the years, physical design and layout of the museum including colors, interior/exterior, arrangement of artifacts, audio/visuals guides, tips are playing key roles in improving the user experience.
Museum visitors typically want to cover more in a short time, and keeping all types of visitors engaged is tedious, especially the younger ones who are well equipped today’s gadgets, and for them traditional brochures and signage methods may not work well. So museums are finding ways of evolving user experience with technological advancements, earlier paper based brochures, navigation maps, tips are now converting into smart touch based displays, websites, or even to the sensor based touch-less interactions. Mobile apps or smart devices are replacing the traditional audio taps. Now, navigating through the museum is getting driven by technology, and this pandemic has induced the need to go virtual. Museum industry is exploring ARVR based technology to provide new ways of interactions and enhance the existing experiences to be ready for future, where the task from the metaversal museum will be quite different, it would demand not only digital (virtual) replicas of the museum itself but also the whole experience need to evolve.
Let’s understand different use cases for the museum industry that can be extended with XR technology as follows.
Extended Navigation — The Museum Explorer
Museums are generally spread in multiple floors, buildings and have large space and an easily accessible navigation path for indoor and outdoor has been a key experience driver. A Museum’s experience has to be a journey, starting from a visitor entering the premise, park vehicle, booking, and entering the museum, visiting different artifacts, till a visitor leaves from the premise.
Traditionally museums provide paper based info brochures, maps, navigational signages, point of attractions, and audio guides in different languages with markers. These ways are not easy to follow for specially abled, or people with non-supported language, these are hard to maintain too
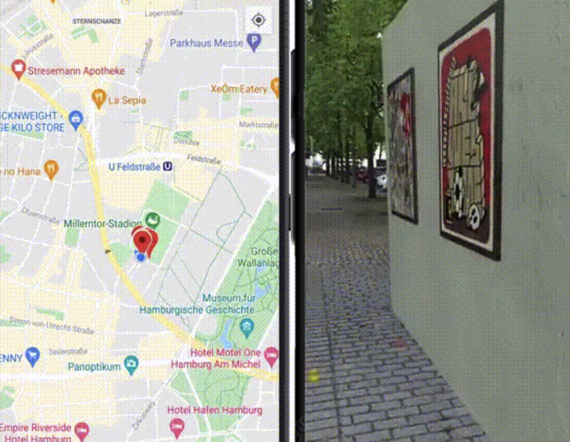
There has been some effort already in building indoor maps from Google similar to standard google map, and now there are number AR applications are being built for Indoor navigation, example is shown below in Fig#1 from OfficeExplorer App from ThoughtWorks. In such case, visitor can use an AR application in a smartphone/tablet or smart glass like ThinkReality A3, and follow the path shown in the phone overlaid on the environments, or they can follow some digital character that appears in the app.
 Fig#1 Indoor navigation using AR
Fig#1 Indoor navigation using AR
The digital character can well talk to the visitor and guide them on the path to the area of interest, or take them to the point of attraction. A visitor may also choose the language of their choice. So instead of maintaining fixed audio taps, devices and paper manuals, museums can now maintain navigational paths digitally, not just that the path can be designed and controlled as per the need, crowd dynamically. They can monitor who is following what path, how much time people spend differently, what area is less explored, and can think of improving the point attraction, so it gets better.
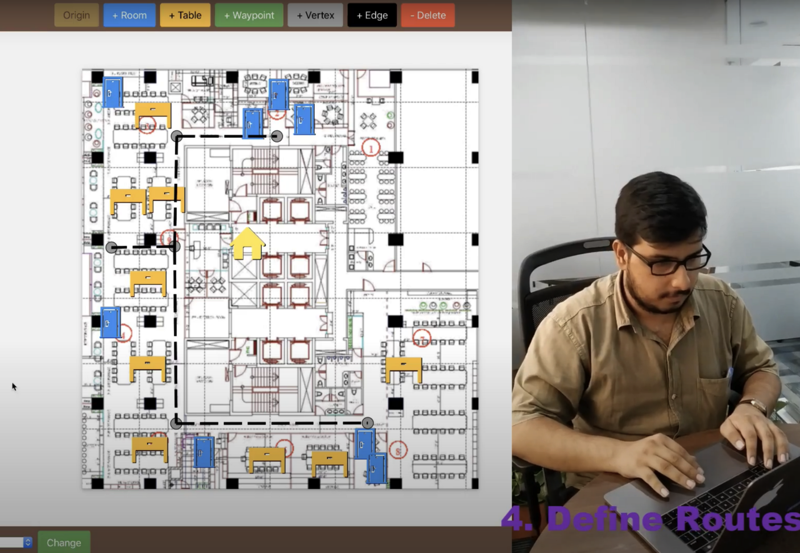 Fig#2 Administrator defines the routes for specially-abled visitors
Fig#2 Administrator defines the routes for specially-abled visitors
Visitors may be shown different navigation paths with time/waiting time, point of attractions etc, and they can choose what suits them best. There can be a dedicated navigation path configured for specially abled, or people who need special attention. Visitors can pre-download the app, and may pre-book the navigations, so they get personalized experience, and enjoy the experience
Extended Artifacts — Tell Me More
The purpose of a museum is to display a set of artifacts from history, science, art, culture or so. Information about these artifacts are typically available in form of brochures, printed boards near the artifacts. Some museums also adapted audio devices/visual displays near the artifacts that can tell information about the artifacts.
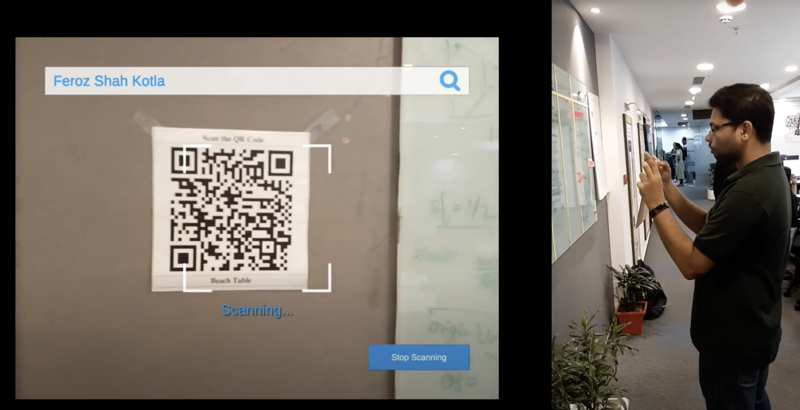 Fig#3 — Scanning a QR code tagged artifact
Fig#3 — Scanning a QR code tagged artifact
In recent times, artifacts getting digitally tagged with QRCode/BarCode, RFID etc. Visitors are using these tag reader phone apps/devices to scan the tags and get the relevant information about the artifacts, this is a less flexible way to manage artifacts information than the traditional paper based crude ways. Fig#4 shows digital information overlaid near the artifact it scanned in Fig#3
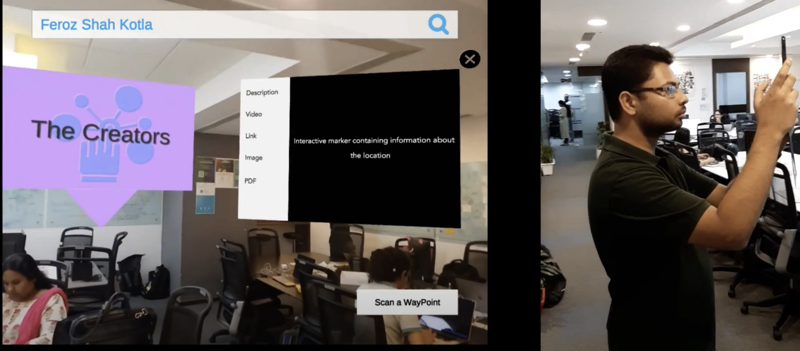 Fig#4 Show the tagged information on the artifact
Fig#4 Show the tagged information on the artifact
With advancements in computer vision and cloud technology, artifacts can now be tagged and persistent as Anchors (e.g Google Cloud Anchor) with respect to the environment. The XR applications can have image and object detection capability that allow showing augmented information directly on the physical objects. For example, Fig 5 shows information about the book (such as booking rating, views, number of pages in the book, reviews etc.) just by looking at this book. This is a snapshot from TellMeMore app built by Thoughtworks
 Fig#5 — Show augmented information on a book just by looking at it from the AR App.
Fig#5 — Show augmented information on a book just by looking at it from the AR App.
The AR app shown in Fig#5 is pre-trained for this book image, similarly all the physical artifacts in a museum can be scanned and an AR app can be pre-trained for that. We can augment any information such as Audio, Video, Image, Text or Document, Website etc at any position relative to the artifact.
This type of application improves visitor experience by bringing contextual information at ease as per their preference. In addition to that, it would allow faster editing/configuring the museum and onboarding new artifacts. We can well measure the telemetry data around usage of content, and see which artifacts are accessed well, what kind of information visitors are interested in, and update the content based on that. It would also save on resources consumed for managing these artifacts, we can divert the effort where it needs attention most.
Extended Visitor Engagement - Look Around
Keeping the visitor engaged is one of the important tasks while designing the museum experience. Traditional ways are getting out dated, and engaging the modern crowd would need modern solutions. Current generation is well versed with smart gadgets, and actively connected on social media.
XR can well help in improving visitor engagement by gamifying the experience. For example introducing games like treasure hunts and pokemon go where visitors can signup and compete in groups. At Thoughtworks, we have built an app named LookARound, that allows users to scan some QR Codes configured at last space, and visitors attempt to collect goodies appearing randomly around the area of attraction.
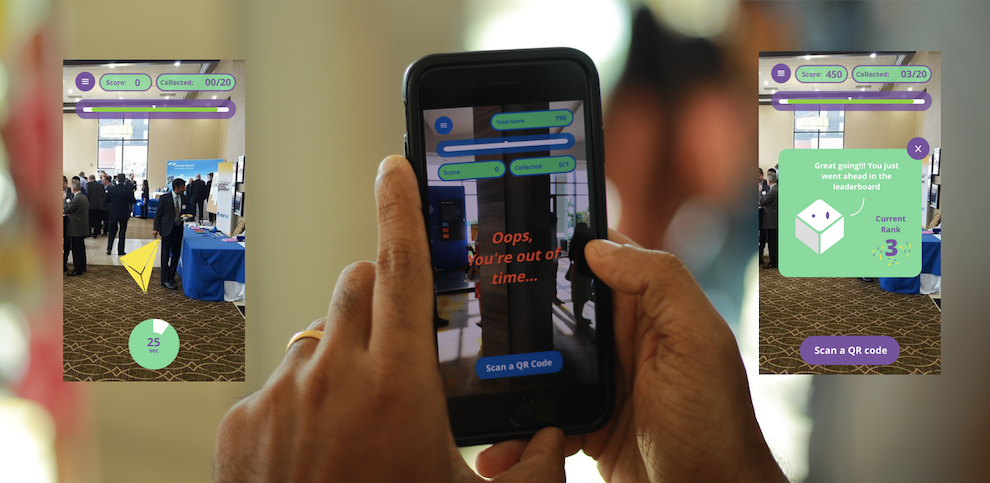 Fig#6 — LookARround app concept for visitor engagement
Fig#6 — LookARround app concept for visitor engagement
This type of app helps in designing large spaces like museums for better customer engagement, in the search of goodies people will explore the places which we want them to visit. Since visitors also come in a group this could be a great app for experience enhancements.
Other ways of improving engagement is to let users provide reviews, feedback, rating on the artifacts directly by looking at artifacts from the XR apps, and other visitors can also see the reviews and ratings, they can also publish these on their social media channels.
There could be experience booths for visitor engagements for having advanced experience like time travel described in the next section. There could be other value added services for taking to food joints, offers, advertisements etc.
 Fig#7 people experiencing XR at a booth
Fig#7 people experiencing XR at a booth
Extended Immersive Experience — Time Travel
We have talked about user experience enhancement in previous sections, and here we will talk about taking that experience to the next level with XR. Visitors look at the artifact wearing a smart glass, it would change the whole environment related to that artifact, it would be like the visitor has traveled in that time, and would see people wearing dresses of that era, see buildings, design of that time. An example of this shown below.
 Fig 8 — Time travel to history in XR
Fig 8 — Time travel to history in XR
This can be further enhanced by multi user collaboration, where a group can join in and be part of the same session. Visitor may choose and try clothings from history and take selfie in those clothes, ornaments, and share these with others
Another example could be, looking at dinosaurs at a museum would take us to the dinosaur era, and the whole environment would change to a jungle and we see dinosaurs roaming around with sounds and animations.
Similarly, if we are in a car museum, and looking at a car, then it can allow visitors to experience the car as follows.
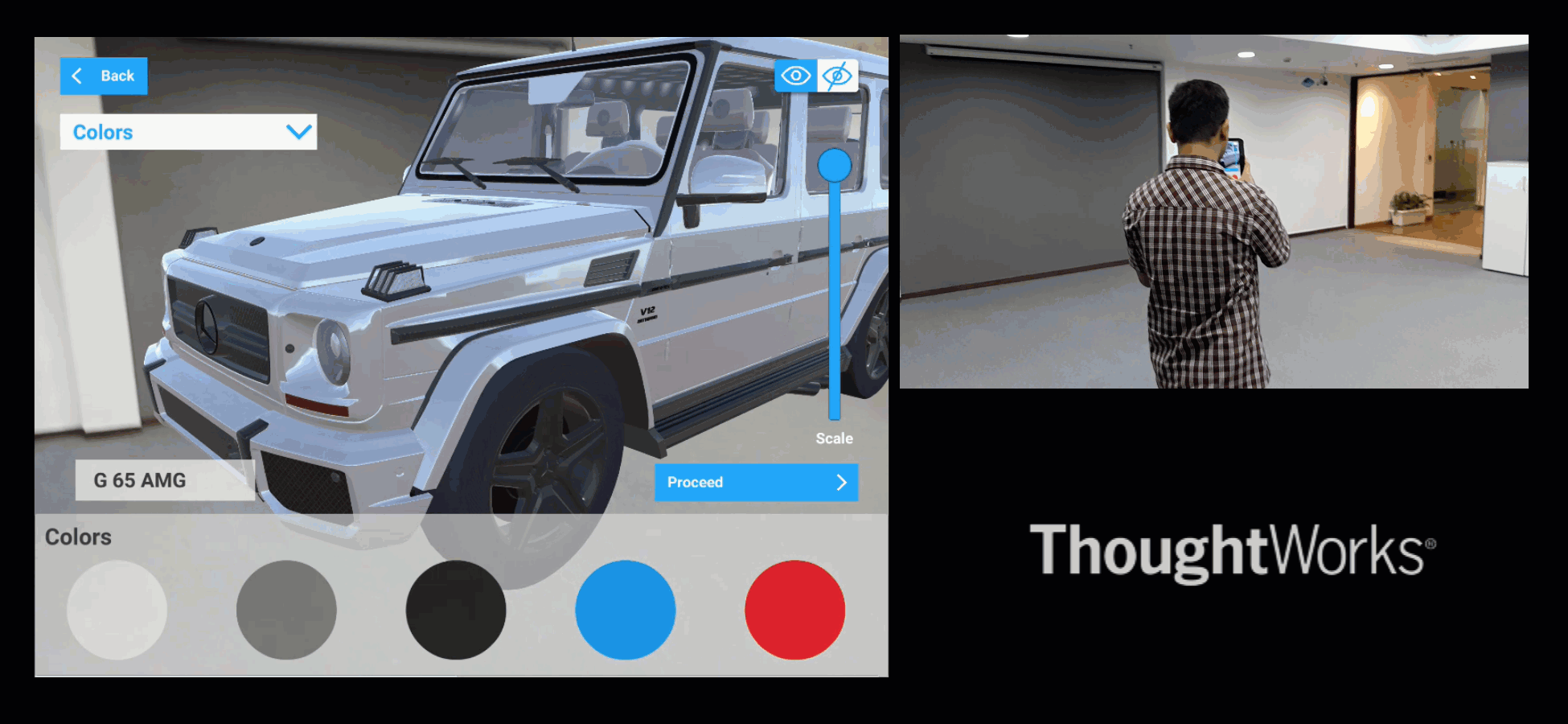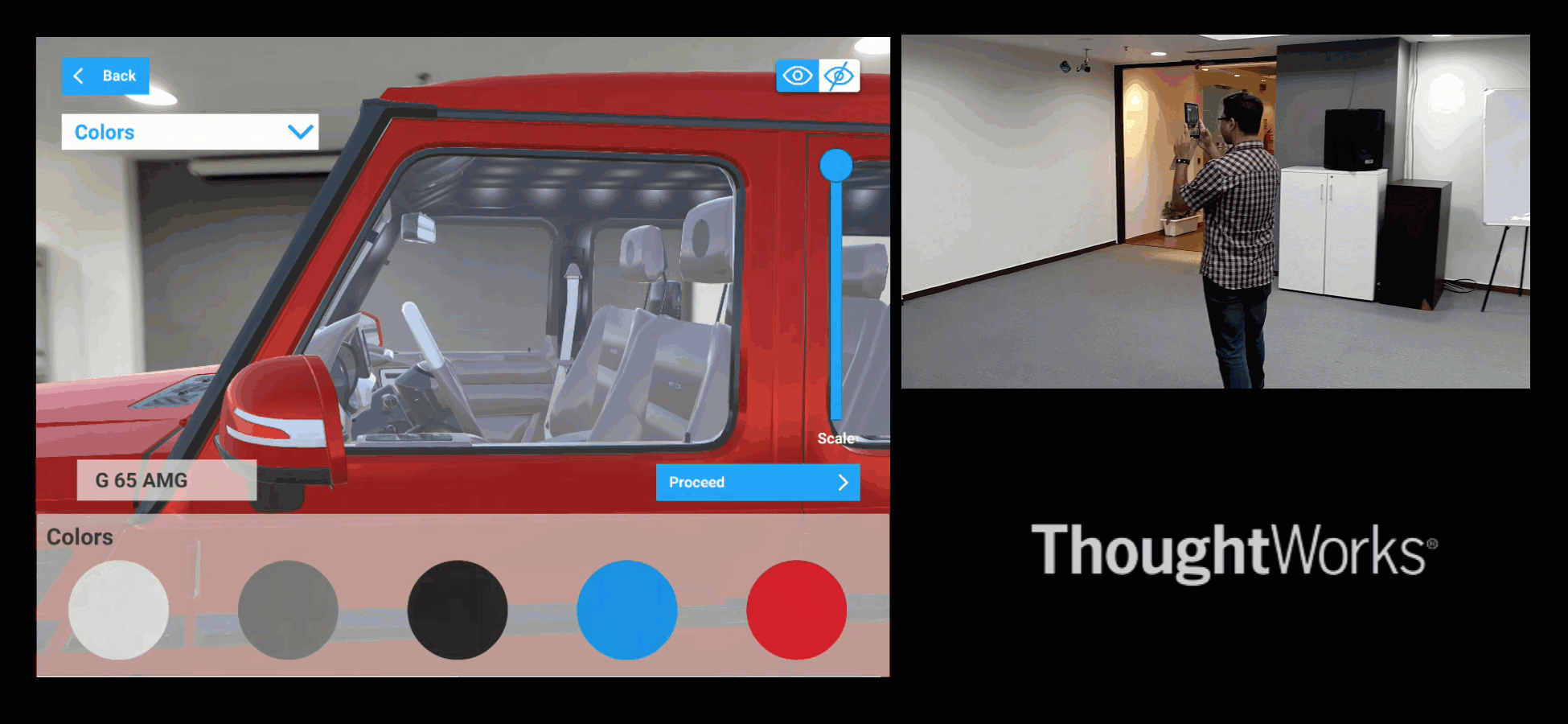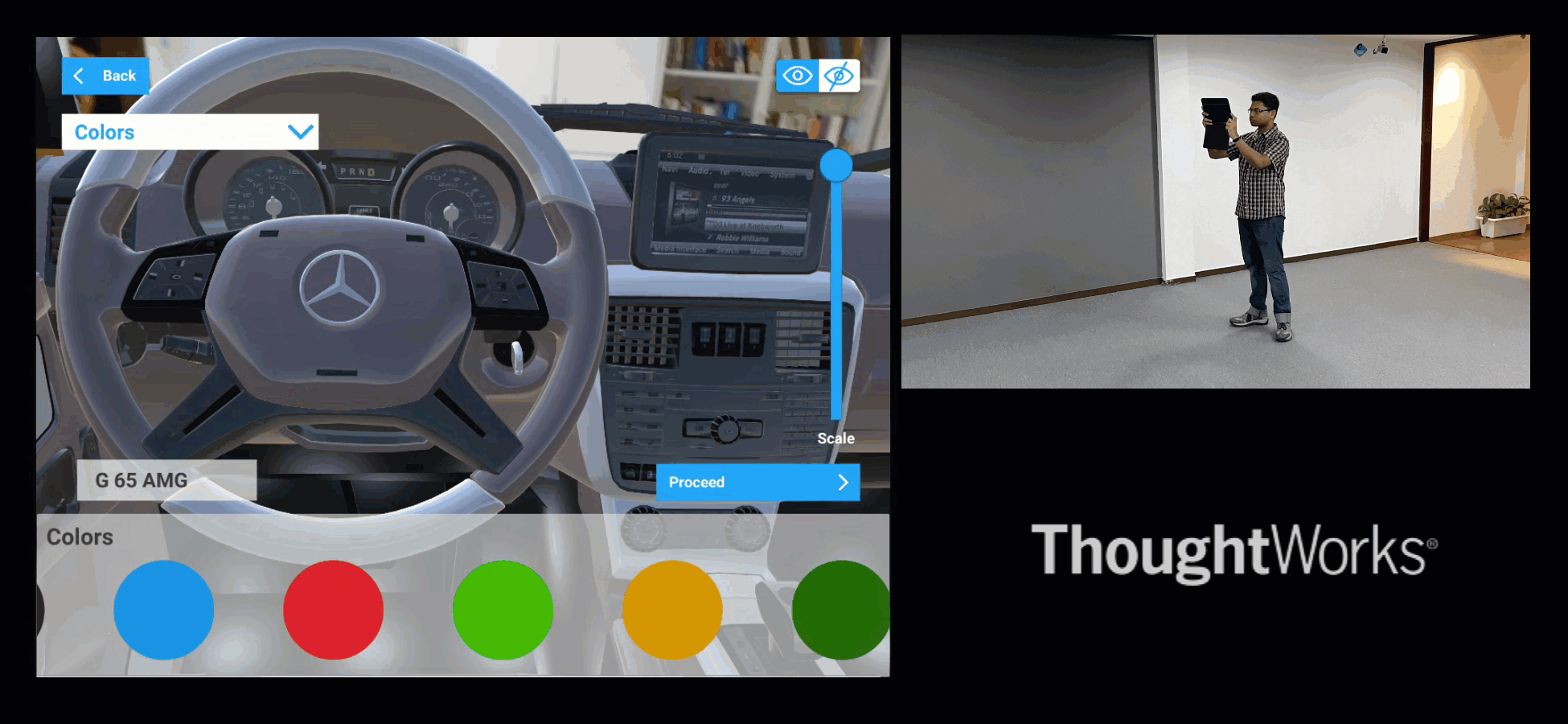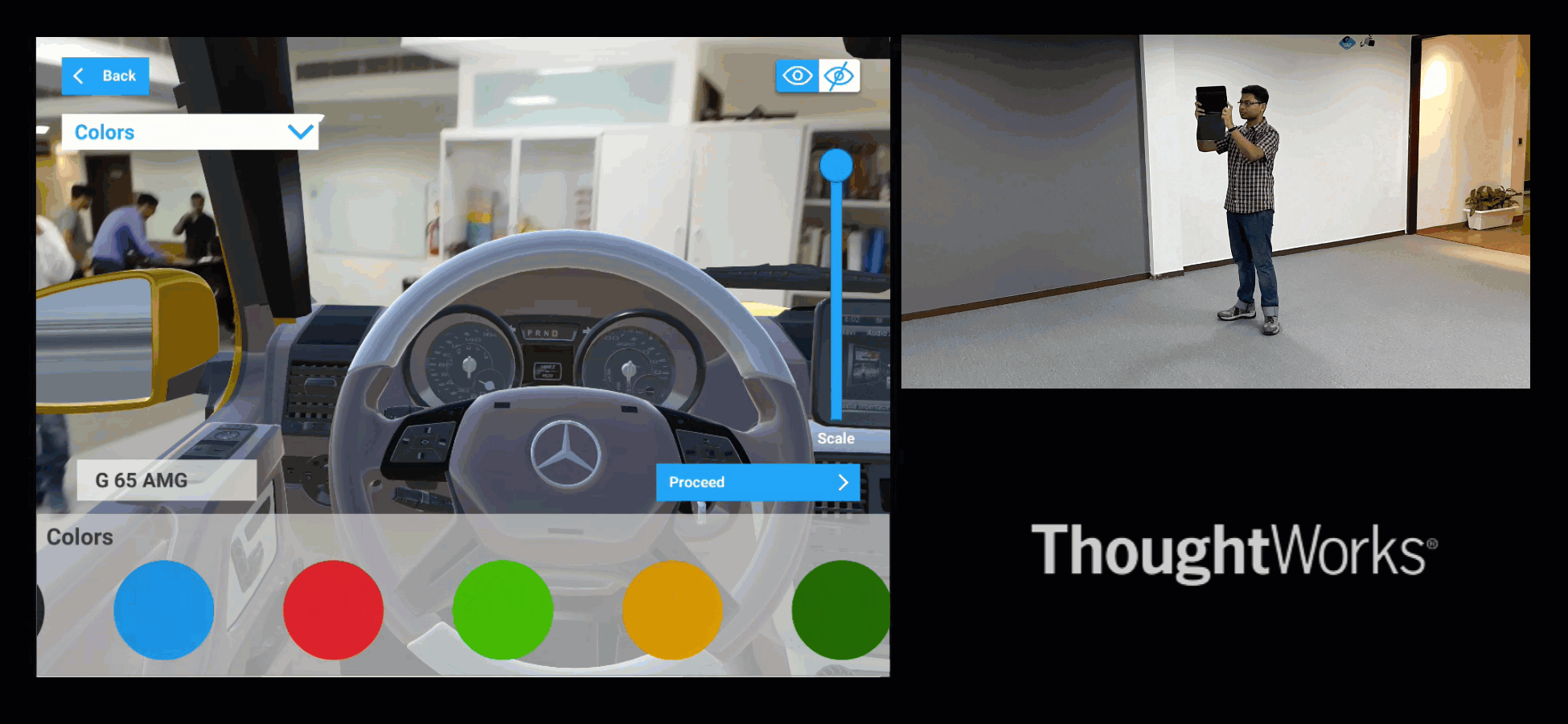 Fig#9 XR visualisation of a Car
Fig#9 XR visualisation of a Car
Zero Museum - Open Museum
Zero museum is a concept coming out with a museum without any physical artifacts, we still have a physical museum but with empty space. Artifacts are shown all virtual, either projected in 3D or shown via smart headsets or AR/VR enabled phone/tablets.
This is a very interesting concept, and the same space can be used for different types of museum, and even at a time multiple visitors can see the same place differently.
Another concept of museum is coming to think of the museum as a city scale experience, like turning all parks or open space of the city into museums or art galleries, where people can search such places and go there to experience it . In fact people may also contribute in submitting the content.
Virtual Museum
Last but not the least, Virtual Museum, where the whole museum experience can be replicated virtually. There are multiple ways of doing that. Visitors can experience it directly on a web browser, and access the museum as a 360 degree tour, example here.
or users can try experiencing a museum in virtual reality headsets. They can walk inside a museum using a controller in the device or walk naturally as today’s device may well track the user’s movement.
This experience is not just experiencing the museum artifacts but also it can also replicate people who are visiting the virtual museums at that time, their avatars can come, and interact with you. It is called metaversal museum experience, and nowadays even NFT museum are also getting hyped, which aim to bring artists and the creator community together, and drive the creator economy.
Museums can build VR training and education materials that they will run with schools, and audiences in a studio setup in the premise as additional services.
Conclusion
I have documented the ways to extend the museum experience using XR technology, where users get the enhanced experience using XR enabled phone/tablet or XR smart glasses/headsets. All different types of AR/VR/MR use cases are possible for museums. XR can cater both the audiences who want to physically visit the museum and those who want to experience it remotely. It can provide a touch less/contact less, and safe experience for physical visitors, and for immersive virtual museum experience for the ones who don’t want to come for physical visit or they can’t come due certain medical conditions. Metaverse will also bring new ways of experiencing the museum.
XR brings flexibility to change the museum as per the visitors’ needs, and can provide a very personalized experience. Visitors would see a different theme/style of the museum on every visit, or in future, we will be able to configure museums as per my need.
Happy visiting! Happy learning!
This article is originally published on XR Practices Publication
#xr #ar #vr #mr #usecases #thoughtworks #Enterprise #technology #museum #lenovo