HashMap Performance Improvement in Java 8
- 2 minutes read - 412 wordsHash collision degrades the performance of HashMap significantly. Java 8 has introduced a new strategy to deal with hash collisions, thus improving the performance of HashMaps. Considering this improvement in Java 8 for hash collisions, existing applications can expect performance improvements in case they are using HashMaps having large number of elements by simply upgrading to Java 8.
Earlier, when multiple keys ends up in the same bucket, then values along with their keys are placed in a linked list. In case of retrieval linked list has to be traversed to get the entry. In worst case scenario, when all keys are mapped to the same bucket, the lookup time of HashMap increases from O(1) to O(n).
Improvement/Changes in Java 8
Java 8 has come with following improvement of HashMap objects in case of high collisions.
- The alternative String hash function added in Java 7 has been removed.
- Buckets containing a large number of colliding keys will store their entries in a balanced tree instead of a LinkedList after certain threshold is reached.
Above changes ensures performance of O(log(n)) in worst case scenarios (hash function is not distributing keys properly) and O(1) with proper hashCode().
How linked list is replaced with binary tree?
In Java 8 HashMap replaces linked list with a binary tree when the number of elements in a bucket reaches certain threshold. While converting list to binary tree hashcode is used as a branching variable. If there are two different hashcode in the same bucket, one is considered bigger and goes to the right of the tree and other one to the left. But when both the hashcode are equal, HashMap assumes that the keys are Comparable, and compares the key to determine the direction so that some order can be maintained. It is a good practice to make the keys of HashMap comparable.
This JDK 8 change applies only to HashMap, LinkedHashMap and ConcurrentHashMap.
Performance Benchmarking
Based on a simple experiment of creating HashMaps of different sizes and performing put and get operation by key,
Following results have been recorded.
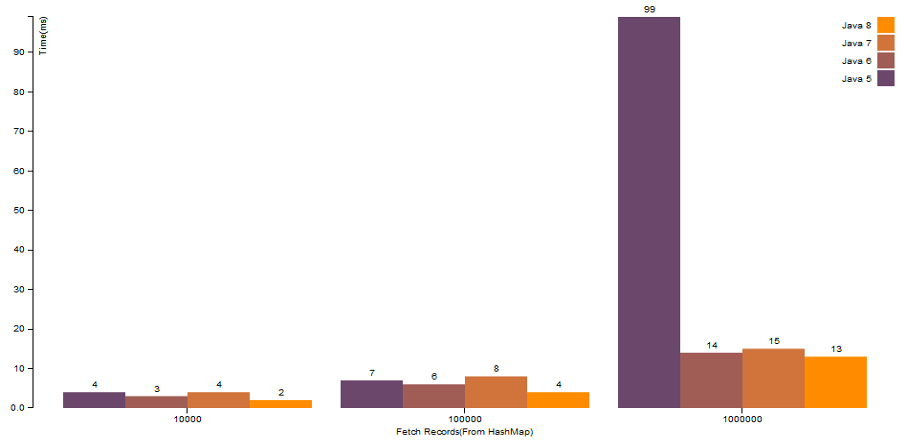
HashMap.get()operation with properhashCode()logic:
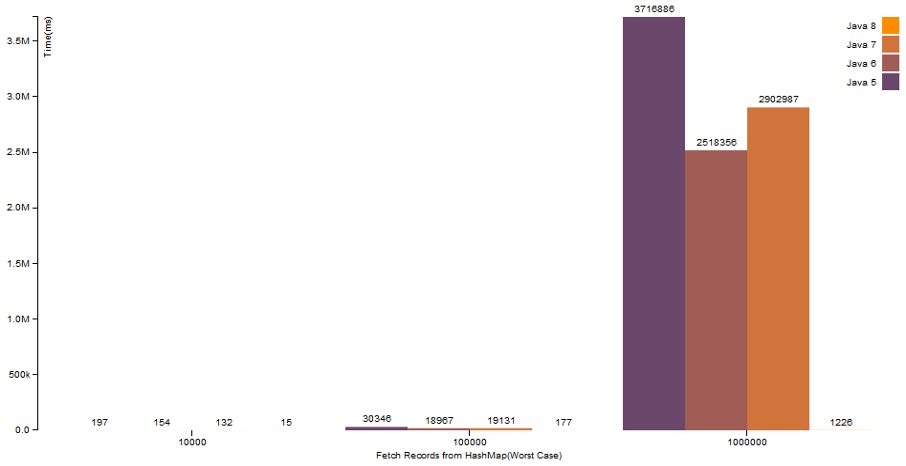
HashMap.get()operation with broken (hashCodeis same for all Keys)hashCode()logic
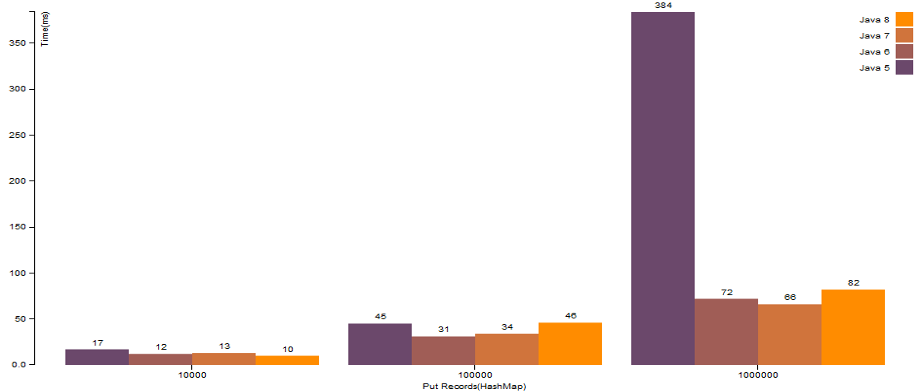
HashMap.put()operation with properhashCode()logic:
HashMap.put()operation with broken (hashCodeis same for all Keys)hashCode()logic
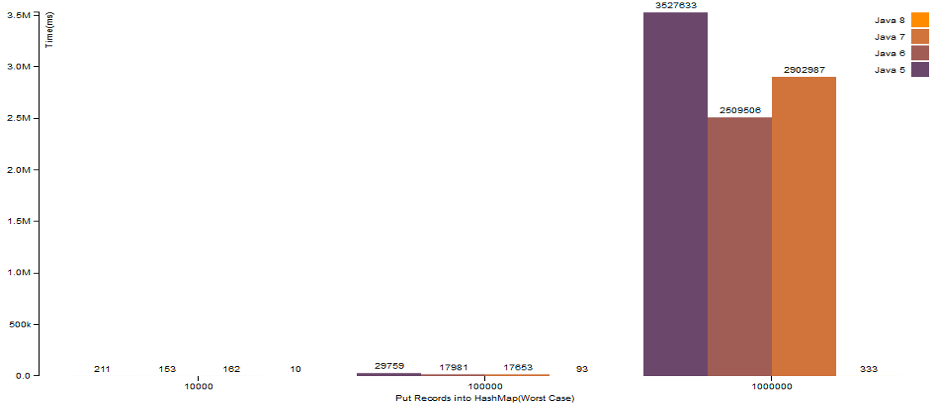
There is a great improvement when there is a map with high number of elements, and even if there are collision, HashMap of Java 8 works much faster than the older versions.